
Today I will continue with the development of my operating system *AlpinOS*. We'll see the first initial tasks to get an SD that will boot into *Raspberry Pi* and we'll know more about how *Alpine Linux* works.
First you must to go to the download area at [alpinelinux.org](https://alpinelinux.org/downloads/) and download the file we need, in this case they make it easy for us, since at the end of the page, there is a specific section for all versions of *Raspberry Pi*. Great!. If you have the Pi 4, use the *aarch64* version. For the older ones, you have *armhf*. Note, the *armhf* version won't work on *Raspberry Pi 4*.
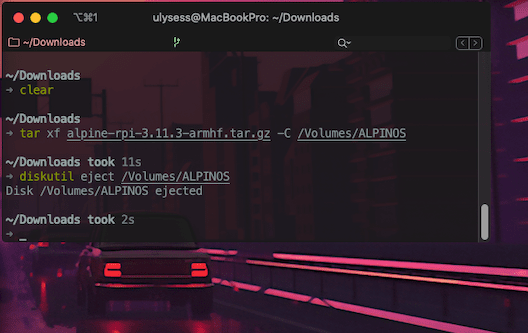
You don't need to burn anything, just copy the downloaded file in a *FAT32* formatted SD and uncompress it, in my case from the folder where I have the file: *tar xf alpine-rpi-3.11.3-armhf.tar.gz -C /Volumes/ALPINES*.
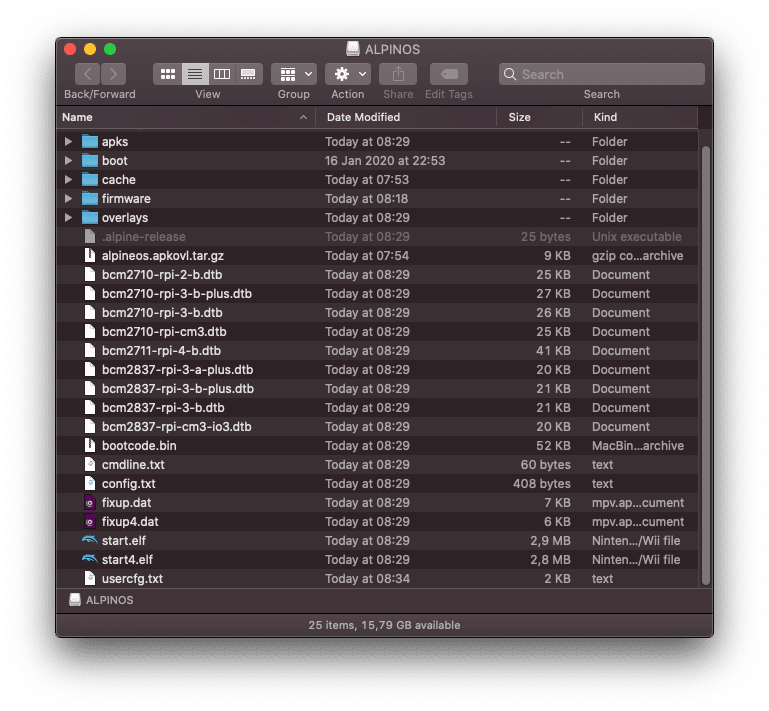
Now we need to add the drivers that are not included with the distribution. Basically what we need to do is copy the */firmware/brmc* folder into the SD. You can do it manually from [firmware-nonfree](https://github.com/RPi-Distro/firmware-nonfree).
You can customize the *config.txt* file, since each monitor and especially the *Raspberry Pi 4*, has its own settings and each one will have its own ready. To do this, you will create a */usercfg.txt* file, since *config.txt* cannot be edited. You have all the commands you can pass on the official website at [raspberrypi.org](https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/config-txt/video.md).
We insert the SD into our Pi, turn it on and in less than 10 seconds you have the operating system ready!.
We're in!. With the *root* user without a password, we now run *setup-alpine* to configure:
keyboard layout.
hostname.
Wired/WiFi network config.
Change root password.
Timezone.
HTTP Proxy.
NTP Client: busybox, openntpd, *chrony* or none.
Mirrors (f) Detect and add fastest mirror, but you can choose random or edit */etc/apk/repositories*.
SSL Server: openssh, *dropbear* or none.
Where store config: floppy (?), *mmcblk0p1*, usb or none.
Apk cache dir. I set the default one on */media/mmcblk0p1/cache*.
Because Alpine runs in memory, all changes are lost with every restart, but we can *"save the game"* as if it were a video game with a utility called *lbu (Local Backup Utility)*. It's very easy to use and we will see it in depth in other post. For now we'll just run *lbu commit* to save the changes and make them available on every reboot.

The time has come when we have an operating system and for our crazy ideas, we're going to want to have a copy of it, so you can use third party applications, *dd* or follow the tutorial I left you some time ago about the *fsarchiver* command in the article [Backup a partition with fsarchive (Linux)](https://misapuntesde.com/post.php?id=253).
We've already made a lot of progress for today. See you next week where we'll update the distribution and start adding the first packages.
Bye!